The main advantage of Office 365 is the ability to access Office applications such as Outlook, OneDrive, Skype for Business, and SharePoint regardless of whether you are directly connected to your organization’s network infrastructure.
Office 365 is centrally hosted in the cloud, so you don’t need to have any server running run it locally (on premises). In other words, Office 365 is hosted remotely. But there are situations where you might be working remotely through a VPN and find that you need to access Office 365 applications.
Office 365 will not behave differently simply because you use a VPN. However, because all network traffic will be redirected to the VPN adapter, you might experience connectivity issues or even complete connectivity loss.
What does a VPN do?
VPN stands for “Virtual Private Network”. It can be thought of as a safe tunnel through which data flows. Basically, it allows your computer to access the internet and any remote services via an encrypted connection. The most commonly used VPN is the Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client.
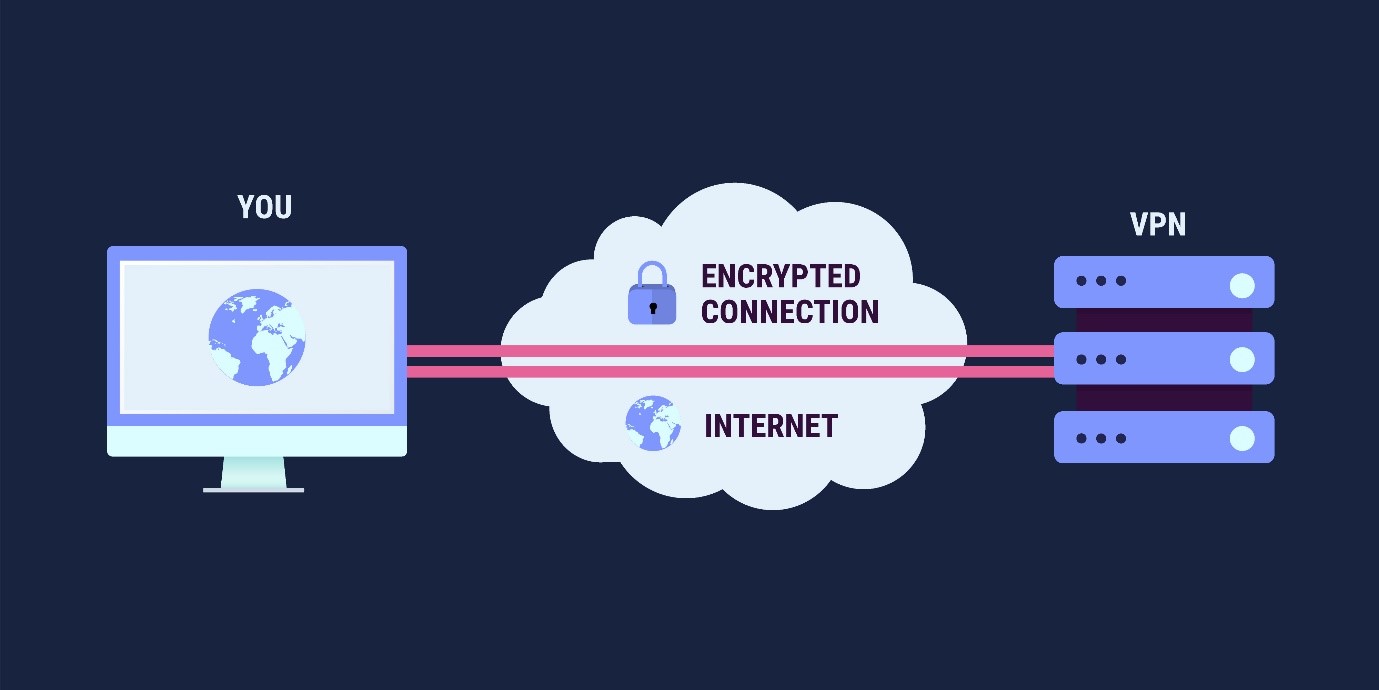
A VPN is commonly used when an employee is working from a remote location and needs to access different organizational resources (e.g., network drives, customer database management software, etc.) that are locally hosted by the company and which require a ciphered, secure connection to protect sensitive information.
Additionally, VPNs are often used by ”external users”, consultants from stakeholder companies who work on Office 365 applications configured with multiple company profiles.
For all these reasons, the standard setups that modern organizations rely on must be able to provide and handle VPN connections.
As mentioned, when you use a VPN, all the network traffic is redirected to the VPN adapter, so Office 365 software may potentially experience connectivity issues, which in turn can affect many other Office 365 features, like meetings creation and Skype for Business desktop sharing.
VPN to Office 365 Connectivity: 7 Troubleshooting Tips
1) Docking Stations

Docking stations are common in office environments where VPN connections are not used.
However, remote employees or external users might work on setups that include docking stations. In many cases, a docking station’s NIC (Network Interface Card) can interfere with the way network traffic is handled through a VPN.
- Take the laptop out of the docking station
- Restart the PC
- Plug the LAN network cable directly into the laptop
- Check if the issue persists
2) Check VPN Software Configuration Settings
Our example is with the Cisco AnyConnect client, but the steps that follow apply to other VPNs as well.
First, note that it’s important to check your VPN settings to ensure that they comply with the organization policies and parameters outlined by your internet service provider or network team.
Also, we need to make sure that our VPN’s default setup is not blocking connections to untrusted servers.
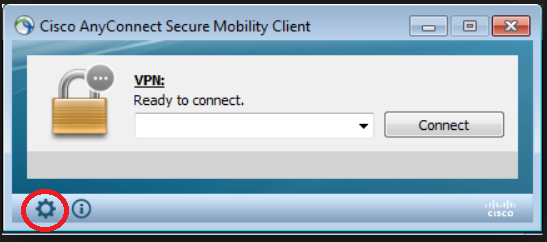
- Open your VPN software
- Connect to your VPN server by providing the credentials when prompted
![Connect to your VPN server]()
- Click on the small gearwheel in your client (Settings)
- On the Preferences tab, make sure the box “Block connections to untrusted servers” is unchecked
![Block connections to untrusted servers]()
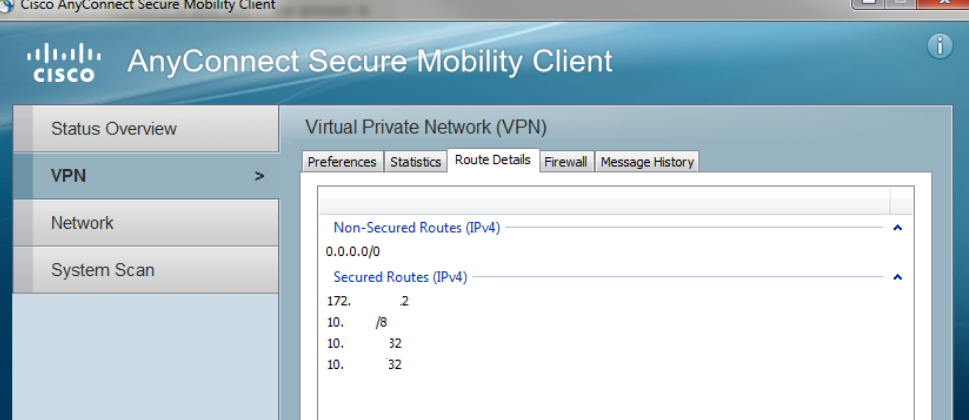
- Next, select the tab titled Route Details
![Route Details]()
Make sure the settings specified here comply with the aforementioned policies and configuration parameters.
3) Configure your VPN for Split Tunnelling
Split tunneling configuration can sometimes alleviate VPN connectivity issues in Office 365 since it avoids bottlenecks (a kind of traffic jam in the network) and saves bandwidth by preventing a section of internet traffic from being redirected to the VPN server.
We need to modify the properties of our VPN connection so that it will not be used as a default gateway for all network traffic.
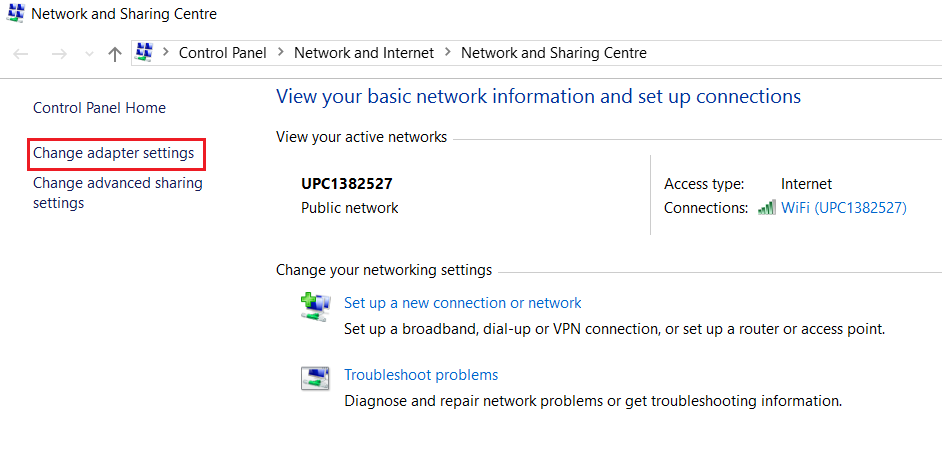
- Open the Control Panel
- Go to Network and Internet
- Select Network and Sharing Centre
- Click on “Change adapter settings” in the left-hand menu
![Change adapter settings]()
- Right click on the VPN connection and select Properties
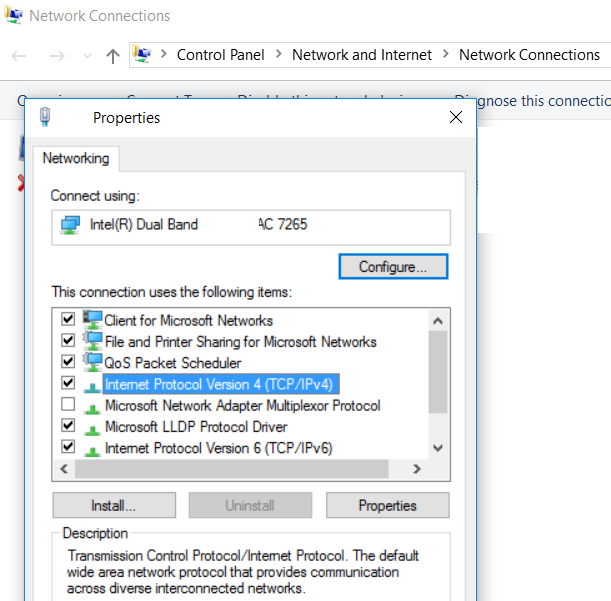
- Select the Networking tab
- Select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4), and click Properties
![Internet Protocol Version 4]()
- Click Advanced
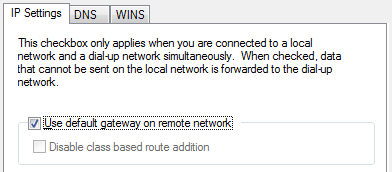
- Uncheck the box for “Use default gateway on remote network”
![Use default gateway on remote network]()
- Click OK
Check if your connectivity to Office 365 has improved. If not, be sure to undo these changes.
4) Proxy Settings
Always be aware of proxy settings, especially within corporate environments. Large infrastructures often rely on proxy network traffic forwarding.
- Open Internet Explorer
- Go to Tools, and select Internet Options
- Select the Connections tab, and click the LAN settings button in the bottom-right corner
- Review your PAC configuration settings
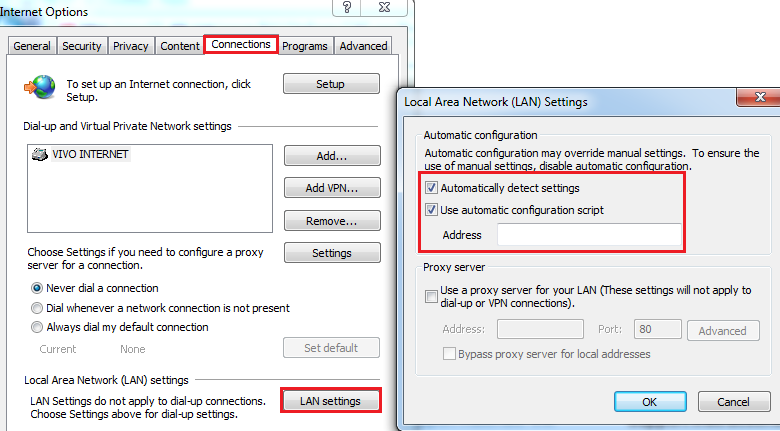
If everything looks good, you can exclude the PAC configuration as the root cause of the issue and proceed with further troubleshooting.
5) Disable the Wireless Network Adapter
In several cases, VPN connectivity issues in Office 365 are caused by the wireless network adapter being enabled. If you are connected via a LAN cable, make sure your wireless network adapter is turned off.
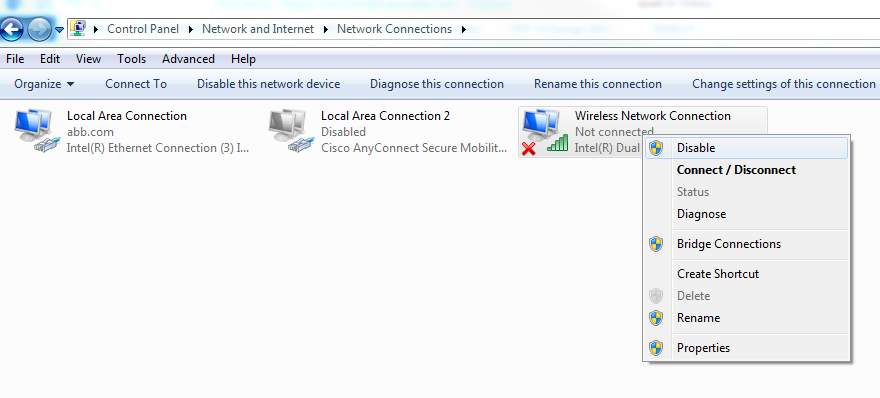
- Go to the Control Panel
- Select Network and Internet, and go to Network Connections
- Right-click on your wireless network connection, and click Disable
6) Office Updates and VPN Connectivity
Sometimes, updating Office is enough to fix VPN connectivity issues.
While the updating process that follows is a bit more complex within a corporate environment (but not necessarily difficult), it is much more straightforward for private Office 365 users.
To begin, open any Office application. We’ll use Word for demonstration purposes.
- Go to File
![Go to File]()
- Select Account from the left-hand navigation
![Select Account]()
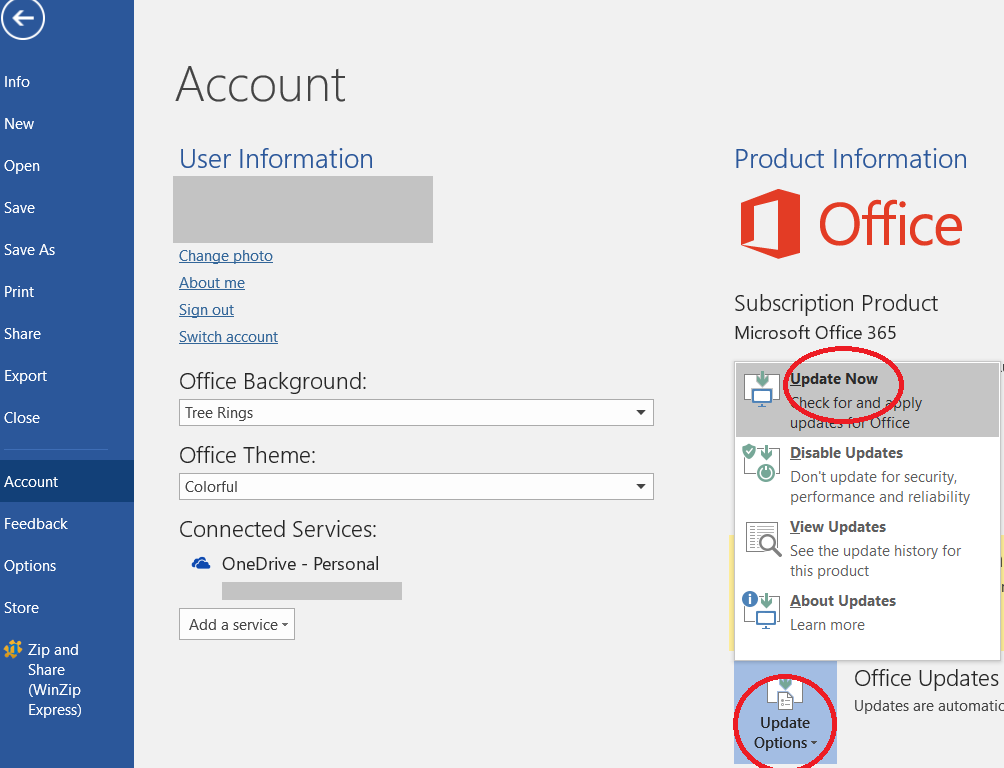
- Select Update Options, and click Update Now.
![Update Now]()
7) Check DNS Service Configuration
VPNs have a side effect: In most cases, when using Office 365 applications while connected to a VPN and outside the corporate network infrastructure (i.e., at home, in a hotel, or anywhere else), the organization’s DNS servers will be used.
But proximity to these servers is crucial for maintaining a stable connection. The Office 365 servers will normally assign the closest available server to the end user. In any case, if your connection to Office 365 has worsened, you should check your DNS settings with either your ISP or your network team.
The steps below show how you can access the DNS settings for your Office 365 environment. This feature is exclusive to Administrators, users who can manage an Office 365 account’s organizational structure by creating, reading, updating, deleting, or modifying Office 365 settings. A regular (non-Administrative) user can’t access the admin portal.
- Go to https://login.microsoftonline.com, and sign in using Admin credentials
- Select the Admin app
![Select the Admin app]()
- Select Domain from the left-hand navigation
![Select Domain]()
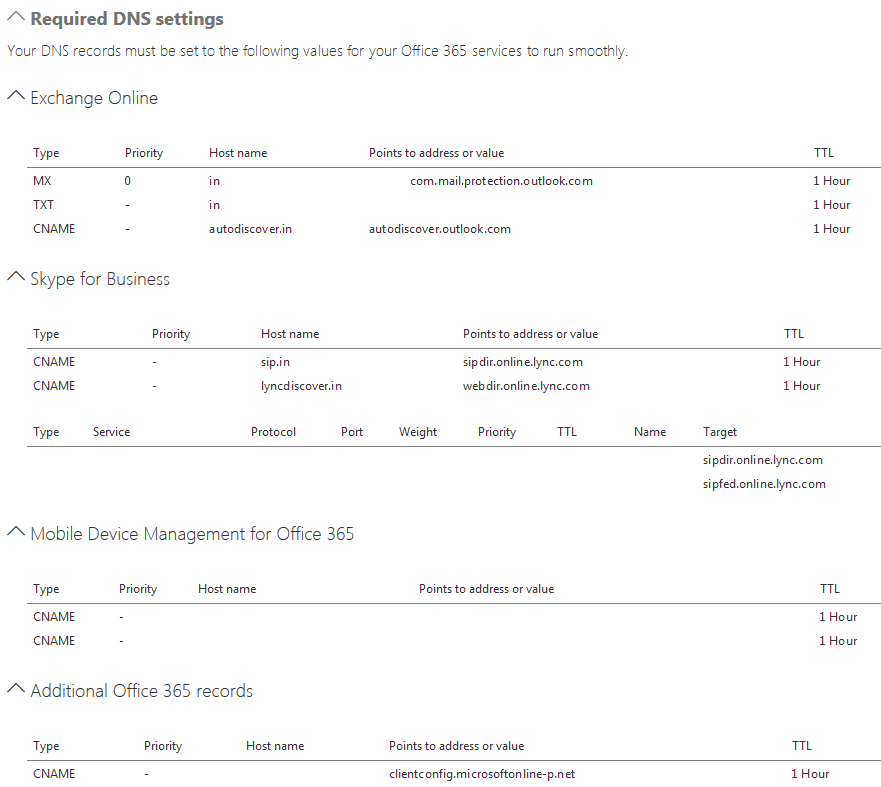
- Go to DNS Settings
Here, you can view the DNS setup for your infrastructure. Make sure these settings are as they should be.
These are just a few of the Office 365 VPN connection troubleshooting steps that we find useful. Do you have any others to add? Let us know in the comments below!
The post How to Make Office 365 Work with VPNs: 7 Troubleshooting Tips appeared first on SherWeb.